The Loch Ness Monster, Production line, Co- Educational Versus Single Sex Classrooms - Reading Answers
8 min read
Updated On
-
Copy link
Want to crack the IELTS Reading test with confidence? Explore this full reading practice test: The Loch Ness Monster, Production line, Co- Educational Versus Single Sex Classrooms, complete with answer key to help you score higher!
Table of Contents

Limited-Time Offer : Access a FREE 10-Day IELTS Study Plan!
The IELTS Reading passage, The Loch Ness Monster, together with the other two IELTS Academic Reading passages – Co- Educational Versus Single Sex Classrooms – forms a full IELTS Reading practice test. This test covers a wide range of topics and question types to help you sharpen your reading skills and get exam-ready. You will have 60 minutes to complete the whole test, which consists of 40 questions in total.
But, before you take the test, learn some tips from this video to get that perfect IELTS Reading score!
The Loch Ness Monster Reading Passage 1


Questions 1-6
Do the following statements agree with the information given in the reading passage?
In boxes 1-6 on your answer sheet write
TRUE, if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE, if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN, if there is no information on this
1 The first reported sighting of the Loch Ness monster was in 1962.
2 It is believed the idea for the Loch Ness monster may have been inspired by other stories of sea creatures.
3 The last person who claims to have seen the Loch Ness monster has video footage.
4 There is evidence to suggest that the Loch Ness monster is related to the plesiosaur.
5 Testing of algae in the loch proved that the food source was insufficient to sustain Nessie.
6 Movement along a fault line could have caused Nessie to rise to the surface.
Questions 7-13
Answer the questions below using NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 7-13 on your answer sheet.
7 When was the first recorded sighting of Nessie?
8 What was Cordon Holmes suspected of doing to the video footage?
9 What common animal may have been caught on camera and mistaken as proof of Nessie?
10 Images of what caused an increase in the number of Nessie enthusiasts?
11 What can visitors hope to see Nessie travel in?
12 Disturbances caused by what could have caused the creature to surface?
13 What has promoted tourism in the Loch Ness area in recent years?
Check out some quick IELTS Exam Preparation Tips for Band Score of 8+ to answer the Reading Answers.
Production line Reading Passage 2



Questions 14-20
Reading Passage 2 has seven paragraphs A-G.
Choose the correct heading for paragraphs A-G from the list of headings below.
Write the correct number i-x in boxes 14-20.
List of Headings
i. A unique focus of TPM
ii. Common issues TPM was established to combat
iii. The statistical weakness of TPM
iv. The introduction of TPM
v. Parallels with a former concept
vi. Types of TPM coordination and training
vii. Implementing TPM
viii. The guiding principles of TPM
ix. The impact of staff involvement
x. Efficiency through involving all employees
xi. The value of mass-production techniques
14 Paragraph A
15 Paragraph B
16 Paragraph C
17 Paragraph D
18 Paragraph E
19 Paragraph F
20 Paragraph G
Questions 21-24
Complete the flowchart.
Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from Reading Passage 2 for each answer.
| Agreement about the 21_________________ offered
by implementing TPM |
| ↓ |
| Nomination/ establish of 22__________ |
| ↓ |
| Education and training of workforce |
| ↓ |
| Creation of 23__________ |
| ↓ |
| Emergence of 24____________ to head group |
Questions 25-28
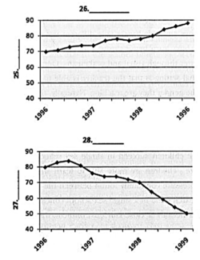
Label the diagram below using words from the box below. USE EACH CHOICE ONLY ONCE.
Write the correct letter A – I next to the questions 25 – 28 on your answer sheet
A Overall equipment effectiveness
B % uptime
C $000s / quarter
D Machine maintenance costs
E % downtime
F $000s / month
G Employee costs
H Wasted resources
I Hours spent cleaning maintaining machinery
Want to improve your IELTS Academic Reading score? Grab Our IELTS Reading Ebook Today!
Co-Educational Versus Single-Sex Classrooms Reading Passage 3
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 29-40, which are based on Reading Passage 3 below.



Questions 29-31
Choose the correct letter, A, B, C or D.
Write your answers in boxes 29 – 31 on your answer sheet.
29 In single-sex classes
A girls learn faster than boys.
B teachers need a wider variety of teaching styles than in a co-education setting.
C some children can thrive due to a more comfortable environment.
D the opposite sex was not missed.
30 Co-education schools
A allow boys and girls to get a more rounded picture of the opposite sex.
B may discourage males from studying certain subjects.
C are falling in popularity.
D have fewer people involved in extracurricular teams and groups.
31 Parents
A must be offered the option of co-educational schools for their children.
B often push boys to succeed in language tasks.
C have reported that single-sex classrooms have helped their child with confidence issues.
D have been influential in the academic performance of single-sex schools.
Questions 32-36
Complete the notes below USING NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS.
Co-educational schools
32intended to reduce gender _______________ , but actually may not be successful.
33started in ______________ but quickly spread.
34allow students to ______________ more easily with opposite sex about general topic.
Single sex schools
35 girls have higher interest in traditionally male dominated ___________________.
36 often have better relationship with __________________.
Questions 37-40
Do the following statements agree with the information given in the reading passage?
In boxes 37-40 on your answer sheet write
TRUE, if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE, if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN, if there is no information on this
37 Single-sex schools are becoming more popular again.
38 Girls do not learn as well as boys through speaking.
39 Surveys have found that coeducational schools are preferred socially.
40 The majority of equal opportunity activists have argued that forcing gender separation on children is unethical.
Want to boost your IELTS score? Enroll in our expert-led IELTS online classes today!
The Loch Ness Monster, Production line, Co- Educational Versus Single Sex Classrooms - Reading Answers
Let’s now review the answers to the questions from the passage in the reading section, and assess your improvement for a high IELTS Reading band score.
The Loch Ness Monster Reading Answers (Passage 1)
| 1 | False
‘The very first sighting of Nessie was as far back as 565 AD’ |
| 2 | True
‘Some people believe that old Scottish myths about water creatures such as Kelpies and water horses have contributed to the idea of this wondrous monster lurking beneath,’ |
| 3 | True ‘2007 brought about the most recent sighting of Nessie. A tourist named Cordon Holmes from Yorkshire visited the Loch Ness waters and claimed he not only saw her but had captured her on video’ |
| 4 | False
‘It has been suggested that Nessie could be related to a prehistoric animal known as a Plesiosaur…although this theory is unsupported by any data |
| 5 | False
‘Despite results that suggest that the fish population was too small, the conclusions drawn were inconclusive’ |
| 6 | False
Disturbances could be mistaken for the Loch Ness Monster. |
| 7 | 565 A.D.
The very first sighting of Nessie was as far back as 565 AD’ Reading Passage 2 |
| 8 | Tampering
‘The video footage has been discredited amid accusations of tampering |
| 9 | Otter
‘…others claim that the image caught by Holmes could be nothing more than a tree trunk or even one of the otters that inhabit the loch’ |
| 10 | A flipper
‘The phenomenon exploded in the second half of the century when photos were publicly released of a ‘flipper’ |
| 11 | A submarine
‘Submarines were sent into the Loch Ness to try to discover more about this creature (and now are actually run as tourist attractions).’ |
| 12 | Road works
‘disruption from nearby road works in the 1930s forced her to move to higher levels’ |
| 13 | The movie industry
‘In 2007, it was estimated that related tourism brought in an estimated £6 million to the region, thanks in part to the attention of the film industry.’ |
Reading Passage 2
| 14 | II
The paragraph refers to the two main problems’ that TPM addresses. |
| 15 | IV
The paragraph talks about when and how TPM was introduced to parts of the world. |
| 16 | X
The paragraph focuses on the importance of not only of managers but of all employees in the application of TPM. |
| 17 | VII
The paragraph refers to the stages of implementing TPM. |
| 18 | VIII
The paragraph talks about the three pillars (guiding principles) of TPM. |
| 19 | V
The paragraph talks about parallels with TQM. |
| 20 | I
The paragraph looks at what TPM sees as a priority (‘unique focus’) |
| 21 | Potential
‘First, there must be universal agreement that the system has the potential to be successful within the company’ |
| 22 | Coordinator ‘Then a specific person or team needs to be appointed to coordinate the changes to TPM…the coordinator.’ |
| 23 | Action teams
‘Once the coordinator is convinced that the workforce is sold on the TPM program and that they understand it and its implications, the first action teams are formed |
| 24 | Team leaders
‘Usually, the TPM coordinator heads the teams until others become familiar with the process and natural team leaders emerge’ |
| 25 | B
See paragraph E |
| 26 | A
See paragraph E |
| 27 | C
See paragraph E |
| 28 | D
See paragraph E |
Co-Educational Versus Single-Sex Classrooms Reading Answers (Passage 3)
| 29 | C
‘Some children succeed in single-sex schools because of the lack of social pressure -children are more able to ¡earn and grow at their own pace without the pressure commonly found between the genders in coeducational schools,’ |
| 30 | B
‘boys in coeducational settings are less likely to study the arts or advanced academic subjects., girls may tend to avoid the sciences and technology subjects’ |
| 31 | A
In order for schools to run single-sex classrooms, they must also offer parents the opportunity to enrol their children in a traditional coeducational classroom,’ |
| 32 | Stereotypes
‘co-education would somehow break down gender stereotypes, but this hasn’t always proved to be the case.’ |
| 33 | Switzerland
‘it was first introduced in Switzerland and swept quickly around most western countries’ |
| 34 | Converse
‘…a coeducational classroom has…helped students to converse about everyday topics with the opposite gender’ |
| 35 | Subjects
‘in single-sex rooms,„ girls are more interested in math and science, subjects generally preferred by boys’ |
| 36 | Teachers
‘Surveys have also shown that a higher percentage of girls in the classroom lower classroom disruption, also creating a better relationship between the students and the teacher’ |
| 37 | True
a significant rise in most western countries of single-sex classrooms |
| 38 | False
girls learn better through oral means |
| 39 | Not given
the surveys only found that the opposite sex was ‘missed’ |
| 40 | False
the text says ‘a small percentage’, not the majority. |
Confused about IELTS prep? Join our exclusive IELTS webinar and clear all your doubts!
Reviewing the answers for The Loch Ness Monster, Production line, Co- Educational Versus Single Sex Classrooms - Reading Answers helps you understand the logic behind each response. Keep practising similar IELTS Reading passages to boost your confidence, accuracy, and IELTS Band Score.
Practice IELTS Reading based on question types

Start Preparing for IELTS: Get Your 10-Day Study Plan Today!
Recent Articles

Nehasri Ravishenbagam

Haniya Yashfeen

Haniya Yashfeen

Haniya Yashfeen



Post your Comments