Raising The Mary Rose - IELTS Reading Answers
11 min read
Updated On
-
Copy link
Improve your Reading skills with the Raising The Mary Rose IELTS Reading Practice Test. Strengthen your skills by checking the answer explanations and also learn proven strategies to tackle every question type with confidence that gets you Band 9!
Table of Contents

Limited-Time Offer : Access a FREE 10-Day IELTS Study Plan!
The Academic Reading passage, Raising the Mary Rose, is an IELTS reading passage that consists of 14 questions. Each task in the IELTS passage is divided into several sets of questions.
You are not completely prepared for the Reading test until you have practiced passages such as ‘Raising the Mary Rose.’ It not only helps you improve your critical reading skills but also introduces you to a wide range of reading passages you may encounter in the actual IELTS exam. So, let's see how easy this passage is for you and if you're able to make it in 20 minutes.
With diligent practice, the IELTS Reading Module can be the top-scoring category for IELTS aspirants. To score well, you must understand how to approach and answer the different question types in the Reading Module.
By solving and reviewing Sample Reading Questions from past IELTS papers, you can ensure that your Reading skills are up to the mark. Take the practice test Raising the Mary Rose below and try more IELTS reading practice tests from IELTSMaterial.com.
The question types found in this passage are:
- IELTS True/False/Not Given (Q. 1-4)
- IELTS Matching Features (Q. 5-8)
- IELTS Diagram Completion (Q. 9-13)
Book a FREE online class to crack more passages just like the ‘Raising The Mary Rose’ in no time!
Raising The Mary Rose - IELTS Reading Passage
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 1-13, which are based on the Reading Passage below.
A On 19 July 1545, English and French fleets were engaged in a sea battle off the coast of southern England in the area of water called the Solent, between Portsmouth and the Isle of Wight. Among the English vessels was a warship by the name of Mary Rose. Built in Portsmouth some 35 years earlier, she had had a long and successful fighting career, and was a favourite of King Henry VIII. Accounts of what happened to the ship vary: while witnesses agree that she was not hit by the French, some maintain that she was outdated, overladen and sailing too low in the water, others that she was mishandled by undisciplined crew. What is undisputed, however, is that the Mary Rose sank into the Solent that day, taking at least 500 men with her. After the battle, attempts were made to recover the ship, but these failed.
B The Mary Rose came to rest on the seabed, lying on her starboard (right) side at an angle of approximately 60 degrees. The hull (the body of the ship) acted as a trap for the sand and mud carried by Solent currents. As a result, the starboard side filled rapidly, leaving the exposed port (left) side to be eroded by marine organisms and mechanical degradation. Because of the way the ship sank, nearly all of the starboard half survived intact. During the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, the entire site became covered with a layer of hard grey clay, which minimised further erosion.
C Then, on 16 June 1836, some fishermen in the Solent found that their equipment was caught on an underwater obstruction, which turned out to be the Mary Rose. Diver John Deane happened to be exploring another sunken ship nearby, and the fishermen approached him, asking him to free their gear. Deane dived down, and found the equipment caught on a timber protruding slightly from the seabed. Exploring further, he uncovered several other timbers and a bronze gun. Deane continued diving on the site intermittently until 1840, recovering several more guns, two bows, various timbers, part of a pump and various other small finds.
D The Mary Rose then faded into obscurity for another hundred years. But in 1965, military historian and amateur diver Alexander McKee, in conjunction with the British Sub-Aqua Club, initiated a project called ‘Solent Ships’. While on paper this was a plan to examine a number of known wrecks in the Solent, what McKee really hoped for was to find the Mary Rose. Ordinary search techniques proved unsatisfactory, so McKee entered into collaboration with Harold E. Edgerton, professor of electrical engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. In 1967, Edgerton’s side-scan sonar systems revealed a large, unusually shaped object, which McKee believed was the Mary Rose.
E Further excavations revealed stray pieces of timber and an iron gun. But the climax to the operation came when, on 5 May 1971, part of the ship’s frame was uncovered. McKee and his team now knew for certain that they had found the wreck, but were as yet unaware that it also housed a treasure trove of beautifully preserved artifacts. Interest in the project grew, and in 1979, The Mary Rose Trust was formed, with Prince Charles as its President and Dr Margaret Rule its Archaeological Director. The decision whether or not to salvage the wreck was not an easy one, although an excavation in 1978 had shown that it might be possible to raise the hull. While the original aim was to raise the hull if at all feasible, the operation was not given the go-ahead until January 1982, when all the necessary information was available.
F An important factor in trying to salvage the Mary Rose was that the remaining hull was an open shell. This led to an important decision being taken: namely to carry out the lifting operation in three very distinct stages. The hull was attached to a lifting frame via a network of bolts and lifting wires. The problem of the hull being sucked back downwards into the mud was overcome by using 12 hydraulic jacks. These raised it a few centimetres over a period of several days, as the lifting frame rose slowly up its four legs. It was only when the hull was hanging freely from the lifting frame, clear of the seabed and the suction effect of the surrounding mud, that the salvage operation progressed to the second stage. In this stage, the lifting frame was fixed to a hook attached to a crane, and the hull was lifted completely clear of the seabed and transferred underwater into the lifting cradle. This required precise positioning to locate the legs into the ‘stabbing guides’ of the lifting cradle. The lifting cradle was designed to fit the hull using archaeological survey drawings, and was fitted with air bags to provide additional cushioning for the hull’s delicate timber framework. The third and final stage was to lift the entire structure into the air, by which time the hull was also supported from below. Finally, on 11 October 1982, millions of people around the world held their breath as the timber skeleton of the Mary Rose was lifted clear of the water, ready to be returned home to Portsmouth.
Questions
Questions 1-4
Do the following statements agree with the information given in the Reading Passage? In boxes 1-4 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
1 There is some doubt about what caused the Mary Rose to sink.
2 The Mary Rose was the only ship to sink in the battle of 19 July 1545.
3 Most of one side of the Mary Rose lay undamaged under the sea.
4 Alexander McKee knew that the wreck would contain many valuable historical objects.
Questions 5-8
Look at the following statements (Questions 5-8) and the list of dates below.
Match each statement with the correct date, A-G.
Write the correct letter, A-G, in boxes 5-8 on your answer sheet.
List of Dates
| A | 1836 | E | 1971 |
| B | 1840 | F | 1979 |
| C | 1965 | G | 1982 |
| D | 1967 |
5 A search for the Mary Rose was launched.
6 One person’s exploration of the Mary Rose site stopped.
7 It was agreed that the hull of the Mary Rose should be raised.
8 The site of the Mary Rose was found by chance.
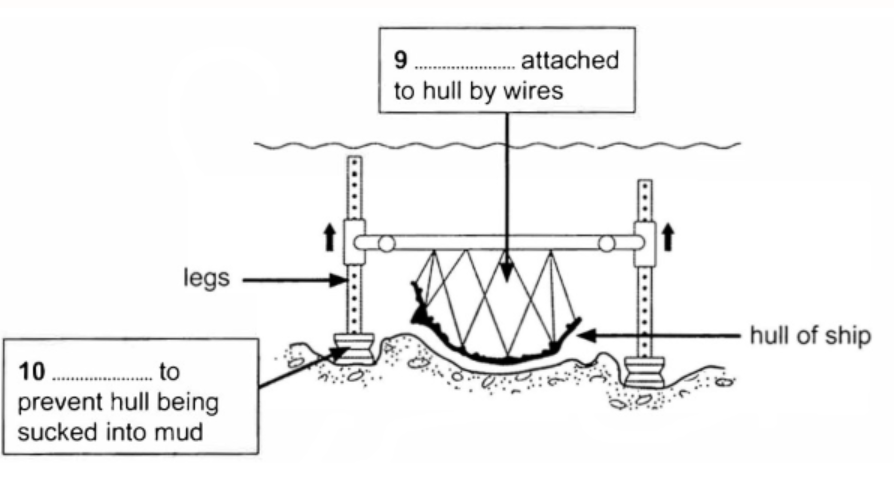
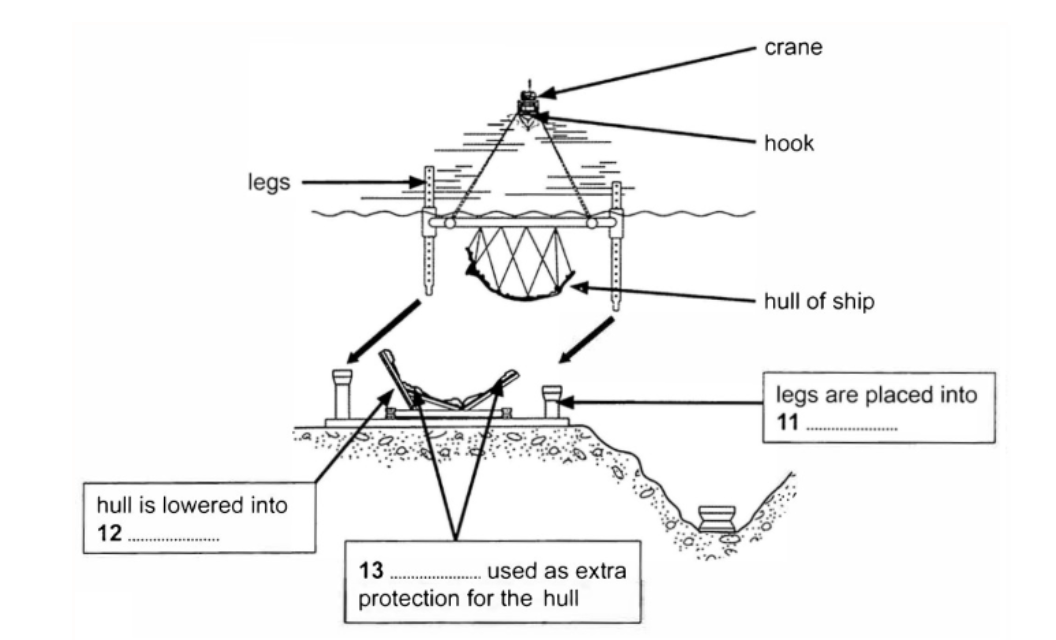
Questions 9-13
Label the diagram below.
Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 9-13 on your answer sheet.
Raising the hull of the Mary Rose: Stages one and two
Raising The Mary Rose - IELTS Reading Answers With Location and Explanation
1 Answer: True
Question type: True/False/Not Given
Answer location: Paragraph A, line 4
Answer explanation: In the specified line, it is stated that “Accounts of what happened to the ship vary: while witnesses agree that she was not hit by the French, some maintain that she was outdated, overladen and sailing too low in the water, others that she was mishandled by undisciplined crew.”. This sentence points out that there are some doubts about what caused the Mary Rose to sink as there are many theories about it. As the statement agrees with the information, the answer is True.
2 Answer: Not Given
Question type: True/False/Not Given
Answer location: N.A.
Answer explanation: As there is no information regarding The Mary Rose being the only ship to sink in the battle of 19 July 1545, the answer is Not Given.
3 Answer: True
Question type: True/False/Not Given
Answer location: Paragraph B, line 4
Answer explanation: In the line of Paragraph B, it is said that “Because of the way the ship sank, nearly all of the starboard half survived intact.” This proves the fact that most of one side (nearly all of the starboard half) of the Mary Rose lay undamaged (survived intact) under the sea. As the statement agrees with the information, the answer is True.
4 Answer: False
Question type: True/False/Not Given
Answer location: Paragraph E, line 3
Answer explanation: In the mentioned line, it is stated “McKee and his team now knew for certain that they had found the wreck, but were as yet unaware that it also housed a treasure trove of beautifully preserved artifacts.”. It can be concluded that Alexander McKee and his team were not aware that the wreck would contain many valuable historical objects (treasure trove of beautifully preserved artifacts). As the statement contradicts the information, the answer is False.
5 Answer: C
Question type: Matching Features
Answer location: Paragraph D, line 2 – line 3
Answer explanation: In Paragraph D, it is said that “But in 1965, military historian and amateur diver Alexander McKee, in conjunction with the British Sub-Aqua Club, initiated a project called ‘Solent Ships’. While on paper this was a plan to examine a number of known wrecks in the Solent, what McKee really hoped for was to find the Mary Rose.”. This points out that in 1965, under a project named ‘Solent Ships’, a search for the Mary Rose was launched. Hence, the answer is C (1965).
6 Answer: B
Question type: Matching Features
Answer location: Paragraph C, line 5
Answer explanation: In Paragraph C, it is said that “Deane continued diving on the site intermittently until 1840, recovering several more guns, two bows, various timbers, part of a pump and various other small finds.”. This points out that Diver John Deane initially thought that the Mary Rose was an underwater obstruction and explored it intermittently until 1840 and recovered several more guns, two bows, various timbers, part of a pump and various other small finds. But later, it was halted for another hundred years. Hence, the answer is B (1840).
7 Answer: G
Question type: Matching Features
Answer location: Paragraph E, line 6
Answer explanation: The specified line states that “While the original aim was to raise the hull if at all feasible, the operation was not given the go-ahead until January 1982, when all the necessary information was available.”. From this reference, it can be said that in January, 1982, it was agreed that the hull of the Mary Rose should be raised as all the necessary information was available. Hence, the answer is G (1982).
8 Answer: A
Question type: Matching Features
Answer location: Paragraph C, line 1
Answer explanation: The indicated line of Paragraph C mentions that “Then, on 16 June 1836, some fishermen in the Solent found that their equipment was caught on an underwater obstruction, which turned out to be the Mary Rose.”. This statement indicates that in 1836, some fishermen found the site of the Mary Rose by chance. Hence, the answer is A (1836).
9 Answer: (lifting) frame
Question type: Diagram Completion
Answer location: Paragraph F, line 3
Answer explanation: The given line of Paragraph F says that “The hull was attached to a lifting frame via a network of bolts and lifting wires.”. From the diagram and the reference sentence, it is clear that the lifting frame was attached to the hull by lifting wires and bolts. Hence, the answer is ‘(lifting) frame’.
10 Answer: hydraulic jacks
Question type: Diagram Completion
Answer location: Paragraph F, line 4
Answer explanation: The given line of Paragraph F says that “The problem of the hull being sucked back downwards into the mud was overcome by using 12 hydraulic jacks.”. It is clear that the hydraulic jacks were attached to the hull to solve the problem of it being sucked in the mud. Hence, the answer is ‘hydraulic jacks’.
11 Answer: stabbing guides
Question type: Diagram Completion
Answer location: Paragraph F, line 8
Answer explanation: The given line in Paragraph F says that “This required precise positioning to locate the legs into the ‘stabbing guides’ of the lifting cradle.”. In light of the fact that the legs are located into the ‘stabbing guides’ of the lifting cradle, the answer is ‘stabbing guides’.
12 Answer: (lifting) cradle
Question type: Diagram Completion
Answer location: Paragraph F, line 8
Answer explanation: In Paragraph F, it is said that “The lifting cradle was designed to fit the hull using archaeological survey drawings…”. This points to the fact that the hull is lowered and fitted into the lifting cradle. Hence, the answer is ‘(lifting) cradle’.
- Answer: air bags
Question type: Diagram Completion
Answer location: Paragraph F, line 8
Answer explanation: The given line in Paragraph F says that “The lifting cradle was designed to fit the hull using archaeological survey drawings, and was fitted with air bags to provide additional cushioning for the hull’s delicate timber framework.” Considering the fact that the air bags provide extra protection to the hulls, the answer is ‘air bags’.
To conclude, we can say that IELTS Reading can be challenging. However, with proper preparation, common errors can be avoided. Additionally, expanding IELTS vocabulary, practicing different question types like the ones in Raising The Mary Rose IELTS Reading passage, and managing time efficiently are essential steps toward improvement.
Practice IELTS Reading based on question types

Start Preparing for IELTS: Get Your 10-Day Study Plan Today!
Recent Articles

Nehasri Ravishenbagam

Haniya Yashfeen

Haniya Yashfeen

Haniya Yashfeen




Post your Comments