The Gulf Stream and Global Warming Reading Answers
Table of Contents

Limited-Time Offer : Access a FREE 10-Day IELTS Study Plan!
The Academic passage, The Gulf Stream and Global Warming Reading Answers, is a reading passage that consists of 13 questions.
With diligent practice, the Reading Module can be the top-scoring category for IELTS aspirants. To score well, you must understand how to approach and answer the different question types in the Reading Module.
By solving and reviewing Sample Reading Questions from past IELTS papers, you can ensure that your Reading skills are up to the mark. Take the practice test The Gulf Stream and Global Warming below and try more IELTS reading practice tests from IELTSMaterial.com.
The question types found in this passage are:
- Multiple Choice Questions (Q. 1-7)
- Flowchart Completion (Q. 8-13)
Reading Passage 1
The Gulf Stream and Global Warming
A Labrador and London lie at about the same latitude, but Labrador is frigid and has only 30 miles of paved roads while London is one of the major centers1 of civilization.2 Why do two places, equidistant from the Arctic Circle, have such disparate climates? The Gulf Stream that flows by the British Isles makes all the difference: Its warm waters make northwestern Europe so abundant with life that palm trees can actually grow on the southern shores of England.
B This life-giving Gulf Stream is warm, salty water, which travels along the surface of the Atlantic Ocean from the Caribbean, along the east coast of the United States, and then veers toward Europe. In the tropics, this water is warmed by the sun and becomes saltier because of the higher rate of evaporation in the heat. The Gulf Stream divides as it travels, but the majority of the stream moves north and east. As it travels past Europe, the Gulf Stream warms the atmosphere, and the prevailing westerly winds bring the warmed air to all of northwestern Europe, making the area suitable for intense agriculture. The Gulf Stream makes it possible for Europe to feed an increasingly large population.
C After the Gulf Stream reaches southeast Greenland and western Iceland, much of the heat of the stream is gone, and the colder, denser water then sinks. The bulk of the Gulf Stream is carried down toward the ocean floor into as many as seven large vortices, called chimneys. They suck the Gulf Stream waters down over a mile deep, where the water is then drawn into another dynamic ocean current. Almost 2 miles below the surface, this cold water current flows in reverse, from the north southward. When this cold water nears the equator, it is again pulled up from the bottom of the ocean as the surface water is heated and starts its journey north. This upwelling brings with it minerals and food from the detritus at the bottom of the ocean to refresh food supplies for fish and other marine creatures.
D This stream of water—the warm water traveling north along the surface and the cold water traveling south along the floor—has become known as the Great Ocean Conveyor Belt. This flow of ocean currents has been extremely important in regulating the temperature of the globe and in making life possible. These currents in the North Atlantic are part of the Great Conveyor Belt that flows through all the oceans of the world. The least stable section of this global current is in the North Atlantic. The Gulf Stream is the most unstable of all.
E Predictions of the effects of global warming on the Gulf Stream are based on computer models, which differ to some extent. But several important facts are known. South of Greenland, there used to be as many as seven chimneys that pulled water from the Gulf Stream down toward the ocean floor. In the last several years, only one remained, and then, in 2007, that one disappeared. The causes for the demise of the chimneys may include the increase in fresh water from glacial melt. In recent winters, glacial melt has released record amounts of fresh water into the oceans. As the North Atlantic waters, including fresh water from rivers as well as the increased amount of glacial melt, mix with the Gulf Stream, the salt water is diluted. Because fresh water is not as dense as salt water, it does not sink, which impairs the natural mechanism for forming the chimneys. As the chimneys have disappeared, the Gulf Stream has slowed. About 30 percent of the water from the Gulf Stream that used to reach Europe travels elsewhere or is lost in the disintegration of the current, a loss of over six million tons of water flow every second. Without a strong Gulf Stream, the slow, cold water of the lower part of the conveyor belt fails to rise, which reduces the circulation of nutrients for marine life. The problem of warming then worsens: As less surface water, which is full of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, siphons into the depths of the ocean, less carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere, thus increasing global warming.
F Ocean sediments and glacial cores show that there have been global swings in temperature in the past. The last Ice Age, when much of North America and northern Europe were covered in glaciers 2 miles thick, occurred when the average temperature dropped about 5 degrees Celsius. That ice age ended about 20,000 years ago. The last “Little Ice Age,” when the average temperature dropped only 1 to 2 degrees Celsius, occurred in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, hitting Europe hardest. At that time, the Gulf Stream had slowed to about half its usual rate.
G Core samples also show that the changes in temperature have been abrupt, not gradual. There would be little time to prepare for the devastating changes resulting from the weakening of the Gulf Stream. The good news is that in the winters of 2008 and 2009, one of the chimneys off southeastern Greenland suddenly burst into action again, bringing the Gulf Stream waters down deep enough to be caught in the conveyor and to keep the ocean currents in the North Atlantic flowing.
1 British: centres
2 British: civilisation
3 British: travelling
Questions 1-7
1 Labrador and London are similar in
A climate.
B distance from the North Pole.
C abundance of wildlife.
2 Europe can support a large population because
A it has a lot of fresh water.
B it is at the proper latitude.
C it has a good climate for farming.
3 When the Gulf Stream reaches the North Atlantic, it sinks because
A it has become colder.
B it has become less salty.
C it is blown by the winds.
4 Ocean currents help make life on Earth possible because they
A enable marine life to travel.
B maintain suitable temperatures.
C regulate glacial melt.
5 In 2007, the number of vortices, or chimneys, that pulled the waters of the Gulf Stream down toward the ocean floor was
A zero.
B one.
C seven.
6 During the most recent Little Ice Age,
A the Gulf Stream slowed down significantly.
B Europe was affected only slightly.
C glaciers covered much of North America.
7 In the past, climate change has happened
A at regular intervals.
B gradually over time.
C very quickly.
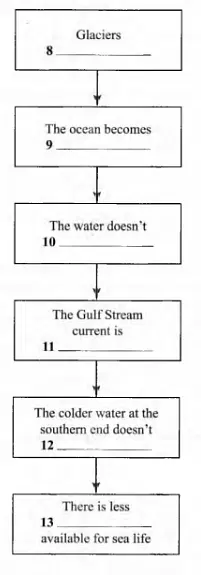
Questions 8-13
The flowchart below shows a possible effect of global warming on the Gulf Stream.
Complete the flowchart using the list of words, A-L, below.
White the correct letter, AL, on lines 8-13 on your answer sheet.
| A less salty | B colder | C warmer | D sink |
| E rise | F weakened | G strengthened | H heated |
| I food | J thaw | K air | L form |
Answer Key
| Question No. | Answer | Question No. | Answer |
| 1. | B | 8. | J |
| 2. | C | 9. | A |
| 3. | A | 10. | D |
| 4. | B | 11. | F |
| 5. | A | 12. | E |
| 6. | A | 13. | I |
| 7. | C |
Explanation
1 Answer: B
Question type: Multiple Choice Question
Answer location: Paragraph A, line 1
Answer explanation: The selected lines say that “Labrador and London lie at about the same latitude…”. This tells us that both these places are equidistant from the North Pole as every place on the east-west lines (latitudes) is the same distance from the equator, the North Pole, and the South Pole. Hence, the answer is B.
2 Answer: C
Question type: Multiple Choice Question
Answer location: Paragraph A, line 4-line 6
Answer explanation: In the quoted lines of Paragraph A, it is said that “Its warm waters make northwestern Europe so abundant with life that palm trees can actually grow on the southern shores of England.”. This points to the fact that Europe can support a large population (abundant with life) because it has a good climate for farming, such that palm trees grow there. Hence, the answer is C.
Unlock Explanations
If you want to have a look at the remaining explanations, sign up!
3 Answer: A
Question type: Multiple Choice Question
Answer location: Paragraph C, line 1 -line 2
Answer explanation: In the quoted lines of Paragraph C, it is said that “After the Gulf Stream reaches southeast Greenland and western Iceland, much of the heat of the stream is gone, and the colder, denser water then sinks.” This proves the fact that when the Gulf Stream reaches the North Atlantic (southeast Greenland and western Iceland), it sinks because it has become colder and denser as the heat is lost. Hence, the answer is A.
4 Answer: B
Question type: Multiple Choice Question
Answer location: Paragraph D, line 3 -line 4
Answer explanation: In the quoted lines of Paragraph D, it is said that “This flow of ocean currents has been extremely important in regulating the temperature of the globe and in making life possible.”. According to this information, ocean currents help make life on Earth possible because they maintain suitable temperatures and enable life around the globe. Hence, the answer is B.
5 Answer: A
Question type: Multiple Choice Question
Answer location: Paragraph E, line 4 -line 5
Answer explanation: In the given lines of Paragraph E, it is said that “In the last several years, only one remained, and then, in 2007, that one disappeared.” This proves that in 2007, the number of vortices, or chimneys, that pulled the waters of the Gulf Stream down toward the ocean floor was reduced to zero. Hence, the answer is A.
6 Answer: A
Question type: Multiple Choice Question
Answer location: Paragraph F, line 5 – line 7
Answer explanation: The mentioned line of Paragraph F says that “The last “Little Ice Age,” … hitting Europe hardest. At that time, the Gulf Stream had slowed to about half its usual rate.” As it is clear that during the last Little Ice Age, the Gulf Stream slowed down significantly (about half its usual rate), the answer is A.
7 Answer: C
Question type: Multiple Choice Question
Answer location: Paragraph G, line 1
Answer explanation: The given line of Paragraph G says that “Core samples also show that the changes in temperature have been abrupt, not gradual.”. It is clear that evidence shows that climate change has happened abruptly (very quickly). Hence, the answer is C.
8 Answer: J
Question type: Flowchart Completion
Answer location: Paragraph E, line 6-line 7
Answer explanation: The quoted lines of Paragraph E claim that “In recent winters, glacial melt has released record amounts of fresh water into the oceans.” It is clear that the glaciers are melting due to global warming (thaw) and releasing fresh water into the oceans. Hence, the answer is J (thaw).
9 Answer: A
Question type: Flowchart Completion
Answer location: Paragraph E, line 7-line 9
Answer explanation: The given lines of Paragraph E say that “As the North Atlantic waters, including fresh water from rivers as well as the increased amount of glacial melt, mix with the Gulf Stream, the salt water is diluted.” As it is clear that the amount of salt decreases (salt water is diluted) due to the increased amount of glacial melt and freshwater mixing the Gulf Stream, the answer is A (less salty).
10 Answer: D
Question type: Flowchart Completion
Answer location: Paragraph E, line 9 – line 10
Answer explanation: The relevant lines of Paragraph E say that “Because fresh water is not as dense as salt water, it does not sink, which impairs the natural mechanism for forming the chimneys.” According to the lines, because the fresh water is less dense, it does not sink. Hence, the answer is D (sink).
11 Answer: F
Question type: Flowchart Completion
Answer location: Paragraph E, line 11
Answer explanation: This specified line of Paragraph E says that “ As the chimneys have disappeared, the Gulf Stream has slowed.” In light of the fact that with the disappearing chimneys, the Gulf Stream is weakened or slowed, the answer is F (weakened).
12 Answer: E
Question type: Flowchart Completion
Answer location: Paragraph E, line 14 – line 15
Answer explanation: The following lines from Paragraph H say that “Without a strong Gulf Stream, the slow, cold water of the lower part of the conveyor belt fails to rise…” From this reference, we can conclude that without the strong Gulf Stream, the colder water fails to rise. Hence, the answer is E (rise).
13 Answer: I
Question type: Flowchart Completion
Answer location: Paragraph E, line 14 – line 15
Answer explanation: The mentioned line of Paragraph H says that “Without a strong Gulf Stream, the slow, cold water of the lower part of the conveyor belt fails to rise, which reduces the circulation of nutrients for marine life.” Based on this reference, we can conclude that without the strong Gulf Stream, the nutrients (food) decrease for marine life. Hence, the answer is I (food).
Practice IELTS Reading based on question types

Start Preparing for IELTS: Get Your 10-Day Study Plan Today!
Recent Articles

Nehasri Ravishenbagam

Haniya Yashfeen

Haniya Yashfeen

Haniya Yashfeen




Post your Comments