Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone - IELTS Reading Answers with Explanations
11 min read
Updated On
-
Copy link
Enhance your IELTS reading band score to 8 or higher using the ‘Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone’ IELTS reading passage along with its answer key. Also, learn to deal with different IELTS reading questions with the tips here and refine your reading strategy.
Table of Contents

Limited-Time Offer : Access a FREE 10-Day IELTS Study Plan!
Are you finding it difficult to complete all three IELTS Reading passages within the allotted one-hour time frame? Time management is one of the biggest challenges test-takers face. The best solution to that problem is to start begin your preparation by taking single passages like ‘Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone IELTS Reading Answers’ from IELTS Reading recent actual tests. With one passage at a time, you can slow down, understand the text thoroughly, and learn to notice patterns.
So, solve a practice passage, ‘Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone IELTS Reading Answers’ followed by three different types of questions, answer explanation and detailed tips focused exclusively on this task.
Passage for Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone IELTS Reading Answers
Now go through the passage for ‘Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone’ Reading Answers given below, and be prepared to solve similar IELTS Reading topics for General and Academic for the reading section.
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 1-13, which are based on the Reading Passage below.
Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone
Breeze-drying is a technique that can help to provide food for astronauts. But it also has other applications nearer home.
Freeze-drying is like suspended animation for food: you can store a freeze-dried meal for years, and then, when you’re finally ready to eat it. You can completely revitalise it with a little hot water. Even after several years, the original foodstuff will be virtually unchanged.
The technique basically involves completely removing the water from some material, such as food while leaving the rest of the material virtually intact. The main reason for doing this is either to preserve the food or to reduce its weight. Removing the water from food keeps it from spoiling, because the microorganisms such as bacteria that cause spoiling cannot survive without it. Similarly, the enzymes that occur naturally in food cannot cause ripening without water, so removing water from food will also stop the ripening process.
Freeze-drying significantly reduces the total weight of the food because most food is largely made up of water; for example, many fruits are more than 80 00% water. Removing this makes the food much lighter and therefore makes transportation less difficult. The military and camping-supply companies freeze-dry foods to make them easier for an individual to carry and NASA has also freeze-dried foods for the cramped quarters on board spacecraft.
The process is also used to preserve other sorts of material, such as pharmaceuticals. Chemists can greatly extend pharmaceutical shelf life by freeze-drying the material and storing it in a container free of oxygen and water. Similarly, research scientists may use freeze-drying to preserve biological samples for long periods of time. Even valuable manuscripts that had been water damaged have been saved by using this process.
Freeze-drying is different from simple drying because it is able to remove almost all the water from materials, whereas simple drying techniques can only remove 90-95%. This means that the damage caused by bacteria and enzymes can virtually be stopped rather than just slowed down. In addition, the composition and structure of the material is not significantly changed, so materials can be revitalised without compromising the quality of the original.
This is possible because in freeze-drying, solid water - ice - is converted directly into water vapour, missing out the liquid phase entirely. This is called ‘sublimation’, the shift from a solid directly into a gas. Just like evaporation, sublimation occurs when a molecule gains enough energy to break free from the molecules around it. Water will sublime from a solid (ice) to a gas (vapour) when the molecules have enough energy to break free but the conditions aren't right for a liquid to form. These conditions are determined by heat and atmospheric pressure. When the temperature is above freezing point, so that ice can thaw, but the atmospheric pressure is too low for a liquid to form (below 0.06 atmospheres (ATM)) then it becomes a gas.
This is the principle on which a freeze-drying machine is based. The material to be preserved is placed in a freeze-drying chamber which is connected to a freezing coil and refrigerator compressor. When the chamber is sealed the compressor lowers the temperature inside it. The material is frozen solid, which separates the water from everything around it on a molecular level, even though the water is still present. Next, a vacuum pump forces air out of the chamber, lowering the atmospheric pressure below to 0.06 ATM. The heating units apply a small amount of heat to the shelves in the chamber, causing the ice to change phase. Since the pressure in the chamber is so low, the ice turns directly into water vapour, which leaves the freeze-drying chamber, and flows past the freezing coil. The water vapour condenses onto the freezing coil in the form of solid ice, in the same way that water condenses as frost on a cold day.
The process continues for many hours (even days) while the material gradually dries out. This time is necessary to avoid overheating, which might affect the structure of the material. Once it has dried sufficiently, it is sealed in a moisture-free package. As long as the package is secure, the material can sit on a shelf for years and years without degrading, until it is restored to its original form with a little hot water. If everything works correctly, the material will go through the entire process almost completely unscathed.
In fact, freeze-drying, as a general concept, is not new but has been around for centuries. The ancient Incas of Peru used mountain peaks along the Andes as natural food preservers. The extremely cold temperatures and low pressure at those high altitudes prevented food from spoiling in the same basic way as a modern freeze-drying machine and a freezer.
Questions for Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone Reading Answers
The passage, Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone Reading Answers, consists of 13 questions, which showcase three different IELTS Reading question types. They are:
- IELTS Reading Note Completion (Q. 1-5)
- IELTS Reading Diagram Completion (Q. 6-9)
- IELTS Reading Summary Completion (Q. 10-13)
Questions 1-5
Complete the notes below.
Choose NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 1-5 on your answer sheet.
|
Uses of freeze-drying:
Freeze-drying
|
Questions 6-9
Label the diagram below.
Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 6-9 on your answer sheet.
A simplified freeze-drying machine
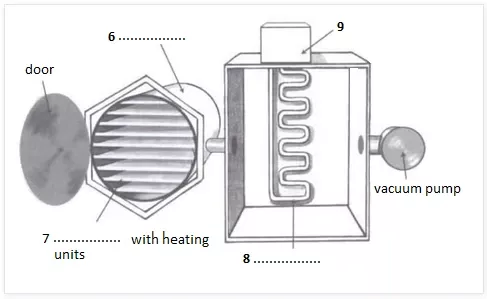
6 …………
7 …………
8 …………
9 …………
Questions 10-13
Complete the summary below.
Choose NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 10-13 on your answer sheet.
Freeze-drying prevents food from going bad by stopping the activity of microorganisms or 10 ………… Its advantages are that the food tastes and feels the same as the original because both the 11 ………… and structure are preserved. The process is carried out slowly in order to ensure that 12 ………… does not take place. The people of one ancient mountain civilisation were able to use this method of food preservation because the conditions needed were present at 13 ………….
Discover fast strategies to master such passages in under 20 minutes.
Join our FREE IELTS webinars!
Answers and Explanations of Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone IELTS Reading Passage
Check out the detailed explanations for the Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone reading passage questions given above and get an idea of how to solve different IELTS Reading question types with examples and improve your reading skills.
| Question number | Answer | Keywords | Location of keywords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | transportation | For example, many fruits are more than 80 00% water. Removing this makes the food much lighter and therefore makes transportation less difficult. | Paragraph C; Lines 1 – 2 |
| 2 | pharmaceuticals | The process is also used to preserve other sorts of material, such as pharmaceuticals. | Paragraph D; Line 1 |
| 3 | manuscripts | Even valuable manuscripts that had been water damaged have been saved by using this process. | Paragraph D; Last line |
| 4 | sublimation | This is possible because in freeze-drying, solid water – ice – is converted directly into water vapour, missing out the liquid phase entirely. This is called ‘sublimation’ | Paragraph F; Lines 1 – 2 |
| 5 | simple drying (techniques) | Freeze-drying is different from simple drying because it is able to remove almost all the water from materials, whereas simple drying techniques can only remove 90-95%. | Paragraph E; Line 1 |
| 6 | (freeze-drying) chamber | The material to be preserved is placed in a freeze-drying chamber | Paragraph G; Line 2 |
| 7 | shelves | The heating units apply a small amount of heat to the shelves in the chamber, causing the ice to change phase | Paragraph G; Line 6 |
| 8 | freezing coil | Since the pressure in the chamber is so low, the ice turns directly into water vapour, which leaves the freeze-drying chamber, and flows past the freezing coil. | Paragraph G; Line 7 |
| 9 | (refrigerator) compressor | The material to be preserved is placed in a freeze-drying chamber which is connected to a freezing coil and refrigerator compressor | Paragraph G; Line 2 |
| 10 | enzymes | similarly, the enzymes which occur naturally in food cannot cause ripening without water, so removing water from food will also stop the ripening process. | Paragraph B; Last line |
| 11 | composition | In addition, the composition and structure of the material is not significantly changed | Paragraph E; Line 3 |
| 12 | overheating | The process continues for many hours (even days) while the material gradually dries out. This time is necessary to avoid overheating, which might affect the structure of the material. | Paragraph H; Lines 1 – 2 |
| 13 | high altitudes | The extremely cold temperatures and low pressure at those high altitudes prevented food from spoiling | Paragraph I; Line 3 |
Learn quick solving tips and reading techniques from experts!
Connect with us through our FREE IELTS online classes!
How to Solve the Question Types in the Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone Reading Passage?
Now, let’s check out some IELTS exam preparation tips for achieving a band score of 8+ for each question type in the Astronaut Ice Cream, Anyone Reading Answers. This will help you learn how to approach each question type effectively.
Note Completion
- Read the title and headings of the notes first: Start by reading “Uses of freeze-drying” carefully, as this tells you the topic and limits your thinking to applications, not processes or history. This prevents distraction when scanning the passage and helps you predict likely nouns (e.g. transport, storage, preservation).
- Predict the grammatical form of each answer: Look at the words before and after each blank to predict whether the answer is a noun, noun phrase, or adjective. For example, ‘easy ___ of food items’ clearly requires a noun, helping you reject verbs or adjectives during scanning.
- Scan for paraphrased keywords, not exact matches: Do not look for the same wording as in the notes; instead, scan for ideas such as ‘lighter’, ‘removed water’, or ‘long-term preservation’. IELTS passages almost always paraphrases the notes, so matching meaning is more important than matching words.
- Locate the paragraph, then read one or two lines carefully: Once you find the relevant paragraph (e.g. Paragraph C or D), slow down and read line by line. The answer will usually appear within one sentence of the keyword, not spread across the paragraph.
- Check word limit and grammar before writing: Count the words carefully and ensure you do not exceed three words. Also, check that the completed note reads naturally and grammatically, because incorrect grammar often signals a wrong choice.
Diagram Labelling/Completion
- Study the diagram before reading the passage: Look closely at the diagram labels and arrows to understand what each part does, not just what it looks like. This helps you recognize functional descriptions in the passage, such as ‘connected to’ or ‘flows past’.
- Identify whether the label refers to an object or a process: Most diagram labels in IELTS Reading are concrete nouns (e.g. chamber, coil, shelves). Knowing this prevents you from mistakenly choosing verbs or long descriptive phrases.
- Scan for technical descriptions, not numbers: Diagram answers are usually found in one compact paragraph that explains how the machine works (here, Paragraph G). Focus on sentences describing movement, connections, or components rather than examples or benefits.
- Match position and function, not order: The answers will not necessarily appear in passage order (6–9). Always match what the part does in the diagram with what the text describes, rather than assuming sequence.
- Keep answers exact and concise: Use only the words from the passage and stay within two words. Adding articles or extra descriptors (e.g. a, the, metal) will make the answer incorrect.
Summary Completion
- Read the summary as a complete paragraph first: Before filling any blanks, read the entire summary to understand the logical flow (cause → advantages → process → historical example). This helps you identify whether a missing word refers to a cause, effect, or condition.
- Identify the type of information needed for each blank: Decide whether the blank needs a thing, process, reason, or location. For example, ‘stopping the activity of microorganisms or…’ clearly signals another biological agent, narrowing your search.
- Scan the passage section by section: Summaries usually follow the same order as the passage, so search paragraph by paragraph instead of randomly scanning. This saves time and reduces confusion between similar ideas.
- Focus on paraphrased cause–effect relationships: IELTS summaries rarely copy sentences word-for-word. Pay attention to connectors like ‘because’, ‘so’, ‘therefore’, ‘as a result’, which often signal where summary answers are located.
- Re-check accuracy, limits, and meaning: After filling all blanks, reread the summary to ensure it makes scientific and logical sense. Confirm you have not exceeded the word/number limit and that spelling matches the passage exactly.
In conclusion, we explored the Astronaut Ice Cream Anyone Reading Answers, including specific locations and keywords, to help you confidently answer those often challenging questions. It is important to note that the three question types with this passage reward precision, not speed scanning. So, it would be beneficial for you to practice a variety of IELTS Reading practice tests and improve your weak areas on the IELTS Reading exam.
Useful Links:
- Health In The Wild - IELTS Reading Answers
- Twist in the Tale - IELTS Reading Answers With Explanations
- Bioluminescence - IELTS Reading Answers
- A New Ice Age - IELTS Reading Answers with Explanations
- The Context Meaning and Scope of Tourism - IELTS Reading Answers
- The Concept of Role Theory Reading Answers
- How Does The Biological Clock Tick? IELTS Reading Answers
Practice IELTS Reading based on question types

Start Preparing for IELTS: Get Your 10-Day Study Plan Today!
Explore other Reading Actual Tests

Kasturika Samanta

Prity Mallick

Kasturika Samanta

Kasturika Samanta
Recent Articles

Nehasri Ravishenbagam

Haniya Yashfeen

Haniya Yashfeen

Haniya Yashfeen




Post your Comments