Bricks The Versatile Building Material - IELTS Reading Answer
10 min read
Updated On
-
Copy link
Prepare yourself with the IELTS Reading passage on ‘Bricks The Versatile Building Material’ and get an opportunity to attempt true, false, not given as well as flowchart and diagram completion. Dive into band 8+ strategies to achieve a higher band score.
Table of Contents
- Types of Questions in the IELTS Reading Passage ‘Bricks The Versatile Building Material’
- How to Approach Questions in ‘Bricks The Versatile Building Material’ to Achieve a Band 8+?
- IELTS Reading Passage - Bricks The Versatile Building Material
- Answers with Location and Explanation on IELTS Passage - Bricks The Versatile Building Material

Limited-Time Offer : Access a FREE 10-Day IELTS Study Plan!
Bricks The Versatile Building Material is an Academic Reading passage where you would encounter three question types. With diligent practice, the IELTS Reading Module can be the top-scoring category for you. To score well, you must first understand how to approach and answer the different question types in the Reading Module.
By solving and reviewing Sample Reading Questions like this passage on ‘Bricks The Versatile Building Material’, you can ensure that your reading comprehension skills are up to the mark. However, you must have a strategic study plan so that you are aware of the specific tricks to be used for each question type. It is recommended that you try to answer questions before diving into the actual answers with location and explanation.
Connect with our band 9 IELTS Trainers to crack your IELTS Reading in no time! Book a FREE Demo.
Types of Questions in the IELTS Reading Passage ‘Bricks The Versatile Building Material’
By practising on a regular basis, you will be able to understand different question types. In this reading passage on ‘Bricks The Versatile Building Material’, you will get to learn a different approach for each question type. Remember that attempting to answer questions would help develop your critical thinking, accuracy, and test-day confidence.
The question types found in this passage are :
- IELTS Reading True False Not Given (Q.1 - Q.5)
- IELTS Reading Flowchart Completion (Q.6 - Q.11)
- IELTS Reading Diagram Completion (Q.12 - Q.13)
How to Approach Questions in ‘Bricks The Versatile Building Material’ to Achieve a Band 8+?
Achieving success in this IELTS Reading passage on ‘Bricks The Versatile Building Material’ requires you to utilize a few IELTS Exam Preparation Tips for Band Score of 8+. With a consistent study plan, you will become familiar with the specific tricks on how to approach these three question types. The following suggests some of these strategies which will elevate your band score.
- Instead of reading the entire passage, you can practice skimming for the main idea and scanning for details. These skills will boost your reading speed and also help you develop your comprehension skills as well.
- Put the timer on every time you attempt practice test papers like this passage on ‘Bricks The Versatile Building Material’. In this way, you will become familiar with the Time Management for IELTS Reading.
- Always focus on understanding the context of the sentences where you spot the keywords. Remember not to assume any answers when you find the keyword in the passage since it might be wrong. Try to comprehend the information given in the passage and then compare that with the statements.
- Read the instructions carefully for diagram completion and flowchart completion type of questions. You must ensure that you follow the word limit and answer according to that or else the answer would be wrong.
- Study the diagram and the flowchart first to understand what kind of information is missing. Try to predict the answer as to whether it is a verb or a noun or an adjective based on the missing blank. Therefore, practice the main topics from the IELTS Grammar.
Want to learn how to answer IELTS Reading Diagram Completion Questions? Dive into the video below!
IELTS Reading Passage - Bricks The Versatile Building Material
A. Bricks are one of the oldest known building materials dating back to 7000 BCE. The oldest found were sun-dried mud bricks in southern Turkey and these would have been standard in those days. Although sun-dried mud bricks worked reasonably well, especially in moderate climates, fired bricks were found to be more resistant to harsher weather conditions and so fired bricks are much more reliable for use in permanent buildings. Fired bricks are also useful in hotter climates, as they can absorb any heat generated throughout the day and then release it at night.
B. The Romans also distinguished between the bricks they used that were dried by the sun and air and the bricks that were fired in a kiln. The Romans were real brick connoisseurs. They preferred to make their bricks in the spring and hold on to their bricks for two years, before they were used or sold. They only used clay that was whitish or red for their bricks. The Romans passed on their skills around their sphere of influence and were especially successful at using their mobile kilns to introduce kiln-fired bricks to the whole of the Roman Empire.
C. During the twelfth century, bricks were introduced to northern Germany from northern Italy. This created the ‘brick Gothic period,’ which was a reduced style of Gothic architecture previously very common in northern Europe. The buildings around this time were mainly built from fired red clay bricks. The brick Gothic period can be categorised by the lack of figural architectural sculptures that had previously been carved in stone, as the Gothic figures were impossible to create out of bulky bricks at that time.
D. Bricks suffered a setback during the Renaissance and Baroque periods, with exposed brick walls becoming unpopular and brickwork being generally covered by plaster. Only during the mid-eighteenth century did visible brick walls again regain some popularity.
E. Bricks today are more commonly used in the construction of buildings than any other material, except wood. Brick architecture is dominant within its field and a great industry has developed and invested in the manufacture of many different types of bricks of all shapes and colours. With modern machinery, earth moving equipment, powerful electric motors and modern tunnel kilns, making bricks has become much more productive and efficient. Bricks can be made from a variety of materials, the most common being clay, but they can also be made of calcium silicate and concrete.
F. Good quality bricks have major advantages over stone as they are reliable, weather resistant and can tolerate acids, pollution and fire. They are also much cheaper than cut stonework. Bricks can be made to any specification in colour, size and shape, which makes them easier to build with than stone. On the other hand, there are some bricks that are more porous and therefore more susceptible to damage from dampness when exposed to water. For best results in any construction work, the correct brick must be chosen in accordance with the job specifications.
G. Today, bricks are mainly manufactured in factories, usually employing one of three principal methods – the soft mud process, the stiff mud process and the dry clay process. In the past, bricks were largely manufactured by hand, and there are still artisanal companies that specialise in this product. The process involves putting the clay, water and additives into a large pit, where it is all mixed together by a tempering wheel, often still moved by horse power. Once the mixture is of the correct consistency, the clay is removed and pressed into moulds by hand. To prevent the brick from sticking to the mould, the brick is coated in either sand or water, though coating a brick with sand gives an overall better finish to it. Once shaped, the bricks are laid outside to dry by air and sun for three to four days. If these bricks left outside for the drying process are exposed to a shower, the water can leave indentations on the brick, which, although not affecting the strength of the brick, is considered very undesirable. After drying, the bricks are then transferred to the kiln for firing and this creates the finished product. Bricks are now more generally made by manufacturing processes using machinery. This is a large-scale effort and produces bricks that have been fired in patent kilns.
H. Today’s bricks are also specially designed to be efficient at insulation. If their composition is correct and their laying accurate, a good brick wall around a house can save the occupants a significant amount of money. This is primarily achieved today through cavity wall insulation. Insulating bricks are built in two separate leaves, as they are called in the trade. The gap between the inner and outer leaves of brickwork depends on the type of insulation used, but there should be enough space for a gap of twenty millimetres between the insulating material in the cavity and the two leaves on either side. The air in these gaps is an efficient insulator by itself. Cavity walls have also replaced solid walls, because they are more resistant to rain penetration. Because two leaves are necessary, a strong brick manufacturing industry is essential, so that enough good quality insulating bricks are plentifully available.
Questions 1-5
Do the following statements agree with the information given in the text?
In boxes 1-5 on your answer sheet write:
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
1 Fired bricks are not efficient in countries with hot weather, as they absorb too much heat.
2 Roman brick production was determined by which season it was.
3 The bricks that led to the brick Gothic period in northern Germany were popular with house builders.
4 Buildings showing brickwork were generally not liked during the Renaissance.
5 Some types of bricks can soak up too much water due to their absorbent qualities.
Questions 6-11
Complete the flowchart below.
Write NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the text for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 6-11 on your answer sheet.
Making Hand-made Bricks
Combine the 6……………, water and other ingredients with a 7…………… to the desired consistency.
↓
Using the hand, fill 8…………… with the mixture-coat with 9…………… (provides a better finish) or water to prevent stickiness.
↓
Dry in the sun; try to avoid rain, which will cause marks in the bricks – this will no affect the bricks’ 10……………
↓
Fire the bricks in a 11………..; patent kilns/large-scale
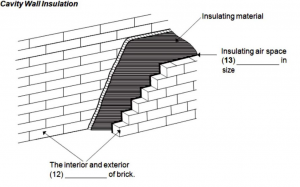
Questions 12 and 13
Label the diagram below.
Write NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER from the text for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 12 and 13 on your answer sheet.
Answers with Location and Explanation on IELTS Passage - Bricks The Versatile Building Material
Now, you will find the answers along with the location of the answers in the passage and the keywords that help you find out the answers. Check out 'Bricks The Versatile Building Material' answers and assess your improvement for a high IELTS Band Score.
|
Answer |
Question Type |
Answer Location |
Answer Explanation |
|
1. False |
True/False/Not Given |
Paragraph A, line 6 & line 7 |
Fired bricks are efficient in hot climates as they absorb and release heat. Hence, the answer is False. |
|
2. True |
True/False/Not Given |
Paragraph B, line 2-line 4 |
Romans preferred to make bricks in spring and aged them for two years. Hence, the answer is True. |
|
3. Not Given |
True/False/Not Given |
N.A. |
No information about brick popularity during the Gothic period. Hence, the answer is Not Given. |
|
4. True |
True/False/Not Given |
Paragraph D, line 1 -line 2 |
Bricks were less popular during the Renaissance as walls were plastered. Hence, the answer is True. |
|
5. True |
True/False/Not Given |
Paragraph F, line 4 -line 6 |
Some bricks are porous and absorb more water. Hence, the answer is True. |
|
6. clay |
Flowchart Completion |
Paragraph G, line 3 – line 5 |
Clay was one of the materials used in the handmade brick process. Hence, the answer is ‘clay’. |
|
7. tempering wheel |
Flowchart Completion |
Paragraph G, line 4-line 5 |
Clay mixture was stirred by a tempering wheel. Hence, the answer is ‘tempering wheel’. |
|
8. moulds |
Flowchart Completion |
Paragraph G, line 6-line 7 |
Clay was hand-pressed into moulds after achieving proper consistency. Hence, the answer is ‘moulds’. |
|
9. sand |
Flowchart Completion |
Paragraph G, line 7-line 8 |
Sand or water was used to coat the brick to prevent sticking. Hence, the answer is ‘sand’. |
|
10. strength |
Flowchart Completion |
Paragraph G, line 10 – line 12 |
Water leaves marks on drying bricks but doesn’t affect strength. Hence, the answer is ‘strength’. |
|
11. kiln |
Flowchart Completion |
Paragraph G, line 12- line 13 |
Bricks were fired in a kiln to finish the process. Hence, the answer is ‘kiln’. |
|
12. leaves |
Diagram Completion |
Paragraph H, line 5 – line 6 |
Gap between inner and outer brick layers is called 'leaves'. Hence, the answer is ‘leaves’. |
|
13. 20 millimetres |
Diagram Completion |
Paragraph H, line 6 – line 8 |
The required gap between layers is 20 millimetres. Hence, the answer is ‘20 millimetres’. |
Enroll into our Free IELTS Webinar and learn more about techniques to improve your reading speed.
Being skilled in various types of questions will be helpful in achieving a higher band score of 8+. With consistent practice, you will improve your comprehension skills so that you can improve your reading speed while finding answers. Applying relevant strategies will increase your confidence, allowing you to remain relaxed during the actual test. Keep practicing to achieve success!
Check More IELTS Reading Answers
Also Check:
Practice IELTS Reading based on question types

Start Preparing for IELTS: Get Your 10-Day Study Plan Today!
Explore other Reading Practice Tests

Kasturika Samanta

Nehasri Ravishenbagam

Prity Mallick
Recent Articles

Nehasri Ravishenbagam

Haniya Yashfeen

Haniya Yashfeen

Haniya Yashfeen





Post your Comments