Roman Tunnels IELTS Reading Answers
13 min read
Updated On
-
Copy link
Struggling with the Roman Tunnels IELTS Reading passage? This article lets you practice it and gives you a step-by-step guide with clear explanations with answer locations, and outstanding tricks from our experts for scoring a band 9 in your final test!
Table of Contents

Limited-Time Offer : Access a FREE 10-Day IELTS Study Plan!
The Academic passage on, ‘Roman Tunnels' consists of 13 questions.
The IELTS Reading can be the top-scoring category for IELTS aspirants with diligent practice. To score well, you must understand how to approach and answer the different question types in the Reading Module.
By solving and reviewing Sample Reading questions from past IELTS papers, you can ensure that your Reading skills are up to the mark. Now take this test and check the Roman Tunnels IELTS Reading Answers below and try more IELTS reading practice tests from IELTSMaterial.com!
The passage, Roman Tunnels, is part of IELTS Academic Reading and the question types found in this passage are:
- Diagram Completion IELTS Reading
- True/False/Not Given IELTS Reading
- Short Answer Questions IELTS Reading
Roman tunnels
The Persians, who lived in present-day Iran, were one of the first civilizations to build tunnels that provided a reliable supply of water to human settlements in dry areas. In the early first millennium BCE, they introduced the qanat method of tunnel construction, which consisted of placing posts over a hill in a straight line, to ensure that the tunnel kept to its route, and then digging vertical shafts down into the ground at regular intervals. Underground, workers removed the earth from between the ends of the shafts, creating a tunnel. The excavated soil was taken up to the surface using the shafts, which also provided ventilation during the work. Once the tunnel was completed, it allowed water to flow from the top of a hillside down towards a canal, which supplied water for human use. Remarkably, some qanats built by the Persians 2,700 years ago are still in use today.
They later passed on their knowledge to the Romans, who also used the qanat method to construct water-supply tunnels for agriculture. Roman qanat tunnels were constructed with vertical shafts dug at intervals of between 30 and 60 meters. The shafts were equipped with handholds and footholds to help those climbing in and out of them and were covered with a wooden or stone lid. To ensure that the shafts were vertical, Romans hung a plumb line from a rod placed across the top of each shaft and made sure that the weight at the end of it hung in the center of the shaft. Plumb lines were also used to measure the depth of the shaft and to determine the slope of the tunnel. The 5.6-kilometer-long Claudius tunnel, built in 41 CE to drain the Fucine Lake in central Italy, had shafts that were up to 122 meters deep, took 11 years to build and involved approximately 30,000 workers.
By the 6th century BCE, a second method of tunnel construction appeared called the counter-excavation method, in which the tunnel was constructed from both ends. It was used to cut through high mountains when the qanat method was not a practical alternative. This method required greater planning and advanced knowledge of surveying, mathematics and geometry as both ends of a tunnel had to meet correctly at the center of the mountain. Adjustments to the direction of the tunnel also had to be made whenever builders encountered geological problems or when it deviated from its set path. They constantly checked the tunnel’s advancing direction, for example, by looking back at the light that penetrated through the tunnel mouth, and made corrections whenever necessary. Large deviations could happen, and they could result in one end of the tunnel not being usable. An inscription written on the side of a 428-meter tunnel, built by the Romans as part of the Saldae aqueduct system in modern-day Algeria, describes how the two teams of builders missed each other in the mountain and how the later construction of a lateral link between both corridors corrected the initial error.
The Romans dug tunnels for their roads using the counter-excavation method, whenever they encountered obstacles such as hills or mountains that were too high for roads to pass over. An example is the 37-meter-long, 6-meter-high, Furlo Pass Tunnel built in Italy in 69-79 CE. Remarkably, a modern road still uses this tunnel today. Tunnels were also built for mineral extraction. Miners would locate a mineral vein and then pursue it with shafts and tunnels underground. Traces of such tunnels used to mine gold can still be found at the Dolaucothi mines in Wales. When the sole purpose of a tunnel was mineral extraction, construction required less planning, as the tunnel route was determined by the mineral vein.
Roman tunnel projects were carefully planned and carried out. The length of time it took to construct a tunnel depended on the method being used and the type of rock being excavated. The qanat construction method was usually faster than the counter-excavation method as it was more straightforward. This was because the mountain could be excavated not only from the tunnel mouths but also from shafts. The type of rock could also influence construction times. When the rock was hard, the Romans employed a technique called fire quenching which consisted of heating the rock with fire, and then suddenly cooling it with cold water so that it would crack. Progress through hard rock could be very slow, and it was not uncommon for tunnels to take years, if not decades, to be built. Construction marks left on a Roman tunnel in Bologna show that the rate of advance through solid rock was 30 centimeters per day. In contrast, the rate of advance of the Claudius tunnel can be calculated at 1.4 meters per day. Most tunnels had inscriptions showing the names of patrons who ordered construction and sometimes the name of the architect. For example, the 1.4-kilometer Cevlik tunnel in Turkey, built to divert the floodwater threatening the harbor of the ancient city of Seleuceia Pieria, had inscriptions on the entrance, still visible today, that also indicate that the tunnel was started in 69 CE and was completed in 81 CE.
Questions 1-6
Label the diagram below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
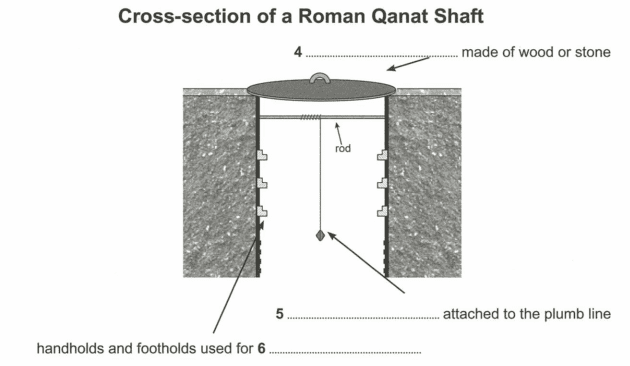
Questions 7-10
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage? In boxes 7-10 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
7. The counter-excavation method completely replaced the qanat method in the 6th century BCE.
8. Only experienced builders were employed to construct a tunnel using the counter-excavation method.
9. The information about a problem that occurred during the construction of the Saldae aqueduct system was found in an ancient book.
10. The mistake made by the builders of the Saldae aqueduct system was that the two parts of the tunnel failed to meet.
Questions 11-13
Answer the questions below. Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer. Write your answers in boxes 11-13 on your answer sheet.
11. What type of mineral were the Dolaucothi mines in Wales built to extract?
12. In addition to the patron, whose name might be carved onto a tunnel?
13. What part of Seleuceia Pieria was the Qevlik tunnel built to protect?
Get set to book a FREE demo for a band 9 in your IELTS Reading now!
Join Now!
Roman Tunnels IELTS Reading Answers With Location and Explanations
Check out the answers and detailed explanations of each question from the Roman Tunnels reading passage given below. They will help you identify areas for improvement, guiding you to modify your preparation strategy and score a higher IELTS Reading band score.
1 Answer: posts
Question type: Diagram Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 2, Lines 3-7
Answer explanation: “In the early first millennium BCE, they introduced the qanat method of tunnel construction, which consisted of placing posts over a hill in a straight line, to ensure that the tunnel kept to its route, and then digging vertical shafts down into the ground at regular intervals.” This explains the diagram how the posts were placed in a straight line on the hill to direct the tunnelling so that it kept to its route.
2 Answer: canal
Question type: Diagram Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 2, Lines 10-11
Answer explanation: “Once the tunnel was completed, it allowed water to flow from the top of a hillside down towards a canal, which supplied water for human use.” The quoted sentence suggests that when the tunnel would be complete, it will allow the water to be used for human consumption by supplying it from the top of the hills and directing it towards a canal as shown in the picture.
3 Answer: ventilation
Question type: Diagram Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 2, Lines 8-9
Answer explanation: “The excavated soil was taken up to the surface using the shafts, which also provided ventilation during the work.” This suggests that the vertical shafts were used to remove the soil and this helped ventilation too as the soil was lifted up to the surface.
4 Answer: lid
Question type: Diagram Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 3, Lines 4-6
Answer explanation: “The shafts were equipped with handholds and footholds to help those climbing in and out of them and were covered with a wooden or stone lid.” This suggests that the lid, shown in the picture, that was used as a covering for the shafts was made up of woods or stones.
5 Answer: weight
Question type: Diagram Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 3, Lines 6-8
Answer explanation: “To ensure that the shafts were vertical, Romans hung a plumb line from a rod placed across the top of each shaft and made sure that the weight at the end of it hung in the centre of the shaft.” This suggests that the weight was hung from the plumbline that was attached to the rod placed across the top of the shaft in order to keep the shafts vertical.
6 Answer: climbing
Question type: Diagram Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 3, Lines 4-6
Answer explanation: “The shafts were equipped with handholds and footholds to help those climbing in and out of them and were covered with a wooden or stone lid.” This suggests that handholds and foot holds helped in climbing through the shafts.
7 Answer: False
Question type: True/False/Not Given
Answer location: Paragraph 4, Lines 1-4
Answer explanation: “By the 6th century BCE, a second method of tunnel construction appeared called the counter-excavation method, in which the tunnel was constructed from both ends. It was used to cut through high mountains when the qanat method was not a practical alternative.” This shows that the counter-excavation method was used whenever the qanat method was not practical and hence, it wouldn’t be right to say that it completely extirpated the qanat method.
8 Answer: Not Given
Question type: True/False/Not Given
Answer location: N/A
Answer explanation: Although there is a mention of this method requiring greater planning and advanced knowledge of surveying, mathematics and geometry, there is no reference in the passage where it is stated that only experienced builders were employed to construct a tunnel using the counter-excavation method.
9 Answer: False
Question type: True/False/Not Given
Answer location: Paragraph 4, Lines 12-17
Answer explanation: “An inscription written on the side of a 428-metre tunnel, built by the Romans as part of the Saldae aqueduct system in modern-day Algeria, describes how the two teams of builders missed each other in the mountain and how the later construction of a lateral link between both corridors corrected the initial error.” This suggests that the information was written on an inscription on the side of the tunnel and not the book.
10 Answer: True
Question type: True/False/Not Given
Answer location: Paragraph 4, Lines 12-17
Answer explanation: “An inscription written on the side of a 428-metre tunnel, built by the Romans as part of the Saldae aqueduct system in modern-day Algeria, describes how the two teams of builders missed each other in the mountain and how the later construction of a lateral link between both corridors corrected the initial error.” This sentence suggests that initially the two parts of the tunnel didn’t have any link and failed to meet in the mountain.
11 Answer: gold
Question type: Short Answer question
Answer location: Paragraph 5, Lines 7-8
Answer explanation: “Traces of such tunnels used to mine gold can still be found at the Dolaucothi mines in Wales.” This shows that the mineral that was mined using such tunnels like the Dolaucothi mines in Wales was gold.
12 Answer: architect’s name
Question type: Short Answer question
Answer location: Paragraph 6, Lines 15-16
Answer explanation: “Most tunnels had inscriptions showing the names of patrons who ordered construction and sometimes the name of the architect.” This shows that besides the name of the patrons, the tunnels had the architect’s name inscripted on them.
13 Answer: the harbour/ harbour
Question type: Short Answer question
Answer location: Paragraph 6, Lines 16-20
Answer explanation: “For example, the 1.4-kilometer Çevlik tunnel in Turkey, built to divert the floodwater threatening the harbor of the ancient city of Seleuceia Pieria, had inscriptions on the entrance, still visible today, that also indicate that the tunnel was started in 69 CE and was completed in 81 CE.” This suggests that the Cevlik tunnel was built to protect the harbor of the city of Seleuceia Pieria.
Tips to Solve the Question Types in Roman Tunnels IELTS Reading Answers
Since now you know the answers to the Reading Answers of Roman Tunnels with explanation, let us check out some quick IELTS exam preparation tips to answer the three types of questions in the reading passage.
Diagram Completion question
The way to solve the diagram completion questions of the IELTS Reading is similar to Table Completion. You will be asked to fill in the blanks in a small passage given in the form of a diagram with the relevant words or numbers. So, let us revise the strategies.
- Read the instructions carefully. It will help you determine the word limit (no more than two, one word, etc) and important terms like ‘using words from the text’ or ‘from the text’. You have to follow these strictly.
- Go through the incomplete diagram first. Also, think about keywords and how they could be represented by synonyms or paraphrasing.
- Locate where the information is by scanning quickly. If you can’t, move on.
- Study the reading text by using the skimming and scanning techniques. It will help to establish the answer quickly. When scanning for your answer, make sure you are thinking about paraphrasing and synonyms.
- The answers appear in the same order as the questions. Also, check your spelling and remember that your answer should be grammatically correct.
True/False/Not Given
In the True/False/Not Given question, you need to provide an answer using ‘True’, ‘False’ or ‘Not Given’ with respect to the statements made. If you believe that the given statement is mentioned in the text and is correct, write ‘True’. If you think the statement is wrong, write ‘False’. And, in case you do not find any piece of information regarding the given statement, write ‘Not Given’. You can use the following strategies:
- Read the question and identify the keywords – Before reading the material, have a look at your list of True, False, and Not Given questions.
- Scan the passage for synonyms or paraphrased words of the keywords – When you have highlighted the keywords, swiftly read the text to look for paraphrases or synonyms using the IELTS Reading keyword techniques.
- Match the highlighted words in the questions with their synonyms in the text – Once you find both sets of keywords, cross-check them to find the answer.
- Identify the answer – Depending on your analysis of the keywords, identify the answer and mark them accordingly.
Short Answer Questions
In Short Answer types, you’ll have to take words from the given passage to write the short answers. In response to the questions, make sure that you take the exact words mentioned in the passage and that you do not exceed the word limit of the answers as instructed. To answer short-answer type questions in IELTS exam, you can use the following strategies:
- Go through the instructions carefully – You will find the word limit for the answers there, which you have to follow strictly.
- Read the questions and highlight the keywords – The next step will be to read the questions to know what keywords or information you have to look for in the passage.
- Use the ‘Wh’ words in the questions – Words like ‘What’, (names), ‘Where’ (place), ‘When’ (time), etc. will enable you to understand the type of information you are looking for.
- Use reading techniques to study the passage quickly – Do not waste your time reading the whole passage. Scan through the passage to find out the keywords or their synonyms. If headers are given, use them to locate the answer easily.
- Check the spelling – Once you find the answer, note the correct spelling in your answer sheet.
Check More IELTS Reading Answers
Practice IELTS Reading based on question types

Start Preparing for IELTS: Get Your 10-Day Study Plan Today!
Recent Articles

Nehasri Ravishenbagam

Haniya Yashfeen

Haniya Yashfeen

Haniya Yashfeen




Post your Comments